AI and the BooM Stack

Lead Image © antoinepham2903, 123RF.com
openEuler prepares for the AI future with a complete software stack tailored for artificial intelligence.
Want more info on openEuler? Download this free focus guide.
It is no secret that tech companies, investors, governments, and futurists are all focused on artificial intelligence (AI). According to experts, the AI technologies emerging now could change the ways we live and work. And technology companies are leading the way, because they know if they don’t embrace this intelligent future, they could be left behind.
Despite all the attention to AI, most Linux systems look much the same as they always have – enterprise distributions tailored for a general, enterprise environment. A few offer variants for edge and cloud, but when it comes to AI, the common approach is to manually add extensions on the fly. Linux is the powerhouse behind the AI revolution, yet many of the adaptations for accommodating AI look like an afterthought. This approach can limit performance and reduce reliability, in addition to taking the time from experts who would prefer to be working on AI applications rather than tweaking the OS environment.
Developers of the openEuler Linux system have taken a different approach: They envision a complete software stack tailored for the needs of AI – a whole system that is AI-ready out of the box.
The developers asked themselves:
- How do we ensure hardware compatibility amid diverse AI scenarios?
- How do we overcome installation difficulties in complex AI software stacks?
- How can the operating system support efficient and reliable AI?
These questions led the openEuler developers to envision a complete software stack that could serve as a universal foundation for AI installations. The Intelligence BooM stack lets you roll out a complete, AI-ready environment in as little as 15 minutes – tuned for performance and end-to-end security, and designed to work with an array of advanced AI-based hardware.
Intelligence BooM
Intelligence BooM is an open source reference implementation of an AI-software stack based on openEuler. The stack integrates seamlessly with mainstream open source solutions at every layer, offering both community implementations and openEuler-optimized alternatives.
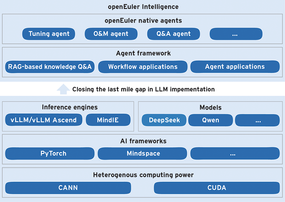
Intelligence BooM (Figure 1) draws together a collection of advanced tools and services to provide a complete solution for AI. Joining these tools into a complete stack can save hours or even days of configuration time – and potentially weeks of troubleshooting. The result is a whole new approach to the problem of AI in Linux: a complete stack that can serve as a native operating environment for AI.
As you will learn in this article, the Intelligence BooM stack doesn’t just support efficient AI workloads; it also offers a comprehensive suite of development tools for building and implementing AI applications. openEuler’s AI development environment is a core strength, supporting seamless and efficient AI development with language tools, training frameworks, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) support, and other components for efficient AI coding.
Also included in the stack are AI-based tools for data management, as well as development frameworks, acceleration tools, and services for supporting AI applications. At the top of the stack is the innovative openEuler Intelligence system [1], a toolkit for developing and implementing AI applications.
The openEuler Intelligence BooM stack is preconfigured and ready for developers who would rather get started on custom AI solutions without building the stack from scratch.
openEuler Intelligence
The top layer of the Intelligence BooM stack is populated with a set of AI tools collectively known as openEuler Intelligence. According to the developers, the goal of openEuler Intelligence is to let the user go “from ideas to AI applications in minutes with a user-friendly visual interface and low-code capabilities.”
openEuler Intelligence (Figure 2) is a key feature of the Intelligence BooM environment, and it is the ingredient that makes openEuler an ideal platform for AI development. The openEuler Intelligence toolkit is preloaded with ready-to-use agents for OS development, deployment, performance tuning, and streamlining developer workflows.
You can also develop your own agents with tools included in the openEuler Intelligence environment. The agent development framework encapsulates AI development capabilities, enabling developers to build custom agent applications with minimal overhead. The framework comes with visual drag-and-drop and multipath retrieval. Developers can access the underlying layers of the stack to efficiently build AI applications. You can upload local APIs through OpenAPI and then visually orchestrate workflows to create your own applications.
openEuler Intelligence also supports RAG, allowing you to parse document formats such as DOCX, PDF, and PPTX to build intelligent Q&A assistants around existing documentation.
openEuler at the Base
The openEuler operating system is tailored for heterogeneous convergence. You’ll find support for a wide range of hardware environments, from x86 to ARM and RISC-V. openEuler also supports the new generation of AI-optimized chips. The Intelligence BooM stack enhances performance for AI workloads with:
- Coordinated scheduling of heterogeneous workloads
- Unified memory management for heterogeneous architectures
- Virtualization and pooling for heterogeneous computing power
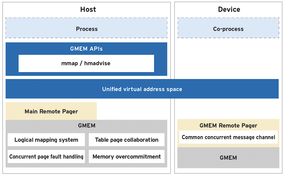
A number of other components are built into the system for seamless AI integration. For instance, LMCache provides a key-value cache layer for memory optimization of large language models (LLMs). FalconFS is a high-performance distributed filesystem for AI workloads. Generalized Memory Management (GMEM) is a centralized management system for connecting heterogeneous memory in distributed environments (see the box entitled “What Is GMEM?”).
| What Is GMEM? |
| New technologies like graphics processing units (GPUs), tensor processing units (TPUs), and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have complicated the task of memory allocation in today’s heterogeneous systems. The good news is that accelerators have their own built-in memory. The challenge is that this memory is separated from the CPU, and conventional techniques for moving data between memory locations can introduce bottlenecks. The Heterogeneous Memory Management (HMM) feature built into Linux can hamper performance and relies on manual tuning. GMEM “combines the two independent address spaces into a unified virtual memory space” (Figure 3) [2]. The GMEM APIs allow for heterogeneous memory programming without memory migrations. |
Data Management
Like any enterprise-grade Linux system, openEuler supports a variety of tools for database management in cloud, edge, HPC, and data center environments. However, the openEuler developers are aware that AI is a special use with special needs for managing vast quantities of data. AI runs on data, and openEuler’s BooM stack integrates a number of tools for meeting the challenge of managing data in AI environments. openEuler can work with openGauss, an open source database management system designed for high performance and high reliability. Also closely integrated with openEuler is pgvector, a PostgreSQL extension that supports the vector similarity search functions essential to many AI systems.
openEuler integrates another important component often used with LLMs and other AI applications: Data-Juicer, which is designed to efficiently generate data recipes used for training AI models.
Containerized Frameworks
openEuler supports a number of popular AI development frameworks in containerized form for easy deployment and integration. In a few clicks, you can prepare a complete development environment for:
- PyTorch
- TensorFlow
- MindSpore
Other images support the CUDA and CANN development environments. This modular, containerized design lets you easily integrate the development tools you need without the clutter of the tools you don’t need – and if your needs change, you can easily adapt.
Acceleration
An accelerated system means faster learning and a shorter response time for AI queries. openEuler integrates several tools for accelerated operation in an AI context. The sysHAX LLM acceleration runtime enhances inference performance. sysHAX improves CPU throughput via NUMA-aware scheduling, parallelized matrix operations, and Scalable Vector Extension (SVE)-optimized inference operators. openEuler also provides the Expert Kit (EK) high-performance framework for scalable Mixture of Experts (MoE) LLM inference. (MoE is a machine learning technique where multiple expert neural networks, acting as learners, divide a problem space for more efficient learning. MoE layers are often used in Transformer models.)
Another powerful acceleration technology built into openEuler is KTransformers (pronounced “Quick Transformers”), an innovative tool developed at Tsinghua University. The Python-centric KTransformers framework offers kernel optimizations and parallel processing strategies. According to the KTransformers developers, “By implementing and injecting an optimized module with a single line of code, users gain access to a Transformers-compatible interface, RESTful APIs compliant with OpenAI and Ollama, and even a simplified ChatGPT-like web UI” [3].
Conclusion
The Intelligence BooM reference stack is a departure point for visualizing the openEuler AI environment. The powerful tools of the openEuler application layer rest on a full stack of open source tools that is tailored and tuned for AI workloads. In addition to the tools described in this article, you will find drivers and software development kits (SDKs) to support out-of-the-box operations for a wide range of AI scenarios. See the box entitled “Performance Matters” for more on the performance tuning tools included with openEuler. The “openEuler Intelligence: A Case Study” box offers an example showing how openEuler Intelligence can bring the power of AI to solving real-world problems.
openEuler runs on a variety of hardware and is supported by a large community of users, including many AI specialists employed in both academia and industry. If you’re interested in learning more about AI in openEuler, contact the openEuler support team at contact@openeuler.io.
This article was made possible by support from openEuler by OpenAtom Foundation through Linux New Media's Topic Subsidy Program.
| Performance Matters |
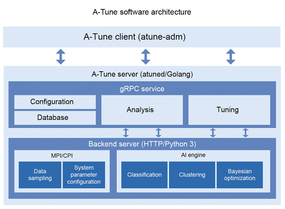
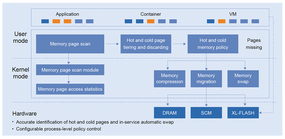
| AI applications place significant demands on performance. The openEuler team has years of experience with tuning HPC systems, cloud environments, and server rooms, and they bring that expertise to the challenge of tuning systems for AI. openEuler includes a number of tools for improving and optimizing performance. For instance, A-Tune (Figure 4) is an AI-powered tuning engine that uses configuration data and performance metrics to automatically tune the system and then continues to iterate using a parameter search algorithm to achieve optimum performance. Another tool, etmem (Figure 5), organizes memory into tiers, automatically routing hot data to high-speed DRAM and cold data to low-speed media. Hybrid Storage Acceleration Kit (HSAK) speeds up I/O for NVMe devices. Also included are custom versions of the GCC and LLVM compilers optimized for the openEuler environment. |
| openEuler Intelligence: A Case Study |
| The Intelligence BooM platform is designed to support custom solutions for practical problems. Sangfor Technologies, for example, recently implemented a patch management solution that leveraged the ready-to-use AI components built into openEuler Intelligence. All enterprise Linux developers face a common problem. The Linux mainline kernel releases an update every 9-10 weeks, with each update containing 2,000-3,000 patches. Most enterprise organizations, however, don’t want the disruption of a full kernel update every 10 weeks. Developers must therefore manually select the relevant patches and integrate them into production branches. This manual update process leads to inefficiencies and bottlenecks. One update can require up to 80 hours of a senior engineer’s time, often leading to error rates exceeding 10 percent. Sangfor wrote their patch management solution around the advanced components built into openEuler Intelligence. The solution leverages Qwen and other LLMs. Standardized templates generate reports, and a syntax analyzer translates code and patch submission into natural language suited for LLM comprehension. The AI-based solution was deployed as an eight-pipeline workflow that reduced the analysis time for 100 patches from 200 minutes to 30 minutes. The direct patch application success rate rose from 90 percent to 98 percent, and the patch analysis speed improved 50 times. Overall, the solution reduced the workload for an update from one person-week to one to two hours. Reducing the time for an update is particularly important in today’s age of heightened security awareness. Sangfor’s AI-based patch management solution reduces the response time for critical vulnerabilities from 14 days to less than 72 hours. By keeping an AI-based development environment close at hand, openEuler enabled a smarter solution to an age-old problem. |
| Info |
|
[1] openEuler Intelligence: https://www.openeuler.org/en/projects/intelligence/ [2] GMEM: https://www.openeuler.org/en/blog/G11N-SIG/20240116-memory-management/20240116-memory-management.html [3] KTransformers: https://kvcache-ai.github.io/ktransformers/ |
| Joe Casad |
| Joe Casad is the editor in chief of Linux Magazine. |