
HONGQI ZHANG, 123RF.com
Configuring the JBoss application server
Who's the Boss?
Java EE provides a development platform based on various software components and services that has become pretty much the standard for developing enterprise applications. Clearly defined APIs allow components from a variety of vendors to collaborate without any trouble. Every Java EE--based application naturally needs the appropriate environment to run in, and the environment must provide the required components and services, such as transaction management, name and directory services, persistency and deployment services, and a security framework (Figure 1). A complete list is available in the Java EE specifications [1].
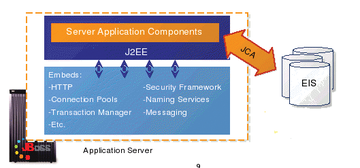 Figure 1: An application server comprises various components that can access an Enterprise Information System.
Figure 1: An application server comprises various components that can access an Enterprise Information System.
On the commercial scene, two widely used heavyweights, IBM WebSphere and BEA WebLogic, support this specification. JBoss provides a Java application server as an open source product under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). It provides all the necessary software components, services, and containers defined by the specification and adds its own server-specific configuration options. For example, JBoss has a container for Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB)
...Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy ADMIN Magazine
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Most Popular
Support Our Work
ADMIN content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you've found an article to be beneficial.




