© Gunnar Pippel, 123RF.com
Reading and understanding database execution plans
Following a Plan
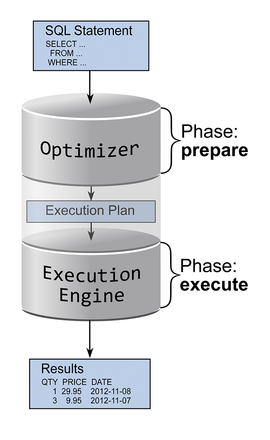
The execution plan (often called the query execution plan or the explain plan) contains the individual steps a database goes through to execute a SQL statement. For example, execution plans provide information on which indexes are used, in which order access to the various tables occurs, and what algorithms are used for joins, sorting, and grouping operations.
The execution plan roughly corresponds to bytecode in scripting languages like Perl or Python – it is used internally to execute SQL statements. Creating an execution plan is sometimes also known as a compiling. However, this is more commonly referred to as the prepare phase (Figure 1). Because the corresponding database component is known as the optimizer or query planner, the terms optimize and plan are also commonly used.
Execution plans are, first and foremost, an internal means to an end, but admins can still view them. Because the execution plan represents processes on a similar level of abstraction as SQL, you can read an execution plan very quickly and – because it's consistently formatted by the database – often even faster than the original SQL statement.
However, execution plan formatting is only uniform for a single database. There is no such thing as a vendor-independent standard. In fact, the execution plans
...Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy ADMIN Magazine
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Most Popular
Support Our Work
ADMIN content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you've found an article to be beneficial.